thick endometrial lining positive pregnancy test|endometrial thickness ultrasound : supplier Abnormally thickened endometrium related to pregnancy is a common finding when doing ultrasound. There are normal causes related to early pregnancy to potentially deadly conditions like ectopic pregnancy. Ultrasound exams routinely evaluate the thickness of the . Resultado da karolrosalin on February 7, 2024: "Monetizando minha liberdade!!! 李 Apenas gratidão no meu coração, obrigada por todos que."
{plog:ftitle_list}
5 de dez. de 2023 · Dois anos de Evoque Av. Goiásl! A Unidade celebrou seu aniversário ontem com gratidão por todos vocês que fazem parte dessa jornada de sucesso. Vamos .
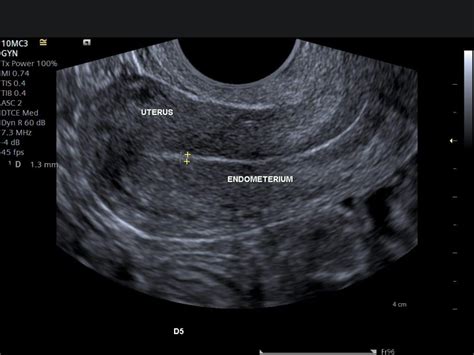
thickness of endometrial lining
Abnormally thickened endometrium related to pregnancy is a common finding when doing ultrasound. There are normal causes related to early pregnancy to potentially deadly conditions like ectopic pregnancy. Ultrasound exams routinely evaluate the thickness of the . To determine whether endometrial thickness and other parameters are useful predictors of normal intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) in the setting of vaginal bleeding and . Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis anatomically restores the uterine cavity in cases of Asherman’s syndrome (AS); however, the extent of endometrial fibrosis could determine the . Endometrial thickness can change throughout a person’s life, such as during pregnancy or menopause. Learn what is typical and how to measure endometrial thickness here.
This results in the observation of the gestational sac adjacent to such a straight uterine cavity in a thick uterine lining - a sonographic sign also known as the intradecidual sign. Why It’s Possible to Have a Positive Pregnancy Test and Heavy Bleeding From Implantation. By Laura Dorwart. Updated on December 13, 2023. Medically reviewed by Renita White, MD. Print. Table of Contents. Causes. . Peak endometrial stripe thickness (EST) has been studied as a predictive factor of pregnancy outcome in IUI, but most studies have focused on CC-stimulated cycles.
This article explains the function of the endometrial lining during menstruation, conception and pregnancy, and menopause. It also discusses normal vs. abnormal endometrial lining thickness, along with conditions that .When the endometrium, the lining of the uterus, becomes too thick it is called endometrial hyperplasia. Learn about the causes, treatment, and prevention of endometrial hyperplasia.Endometrial Hyperplasia: A condition in which the lining of the uterus grows too thick. Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia (EIN): A precancerous condition in which areas of the lining of the uterus grow too thick. Endometrium: The lining of the uterus. Estrogen: A female hormone produced in the ovaries. The decidua is the thick lining of the uterus that forms as a result of progesterone. . Positive pregnancy test; consists of decidua and developing embryo, although the embryo may not be visible .
Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that begins as a growth of cells in the uterus. The uterus is the hollow, pear-shaped pelvic organ where fetal development happens. Endometrial cancer begins in the layer of cells that form the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer is sometimes called uterine cancer. – **Uterine Fibroids**: Non-cancerous tumors that develop within the uterine wall. – **Endometrial Hyperplasia**: A condition characterized by the thickening of the endometrial lining, often due to excess estrogen without progesterone. – **Endometrial Cancer**: Although less common, heterogeneous endometrium can be an early sign of cancer.Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition where the lining of your uterus is abnormally thick. It causes heavy menstrual bleeding. Some types may lead to cancer. . During ovulation, estrogen thickens your endometrium, while progesterone prepares your uterus for pregnancy. If conception doesn’t occur, progesterone levels drop. .
In addition, data were provided concerning CPR (defined as the number of clinical pregnancies that diagnosed by ultrasonographic visualization of one or more gestational sacs after positive human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) tests per cycles), implantation rate (IR, defined as the ratio of the number of gestational sacs to number of embryos . A false positive 4 can happen for a variety of reasons 5 , including using an expired test, having hCG in your body due to recently taking fertility drugs that contain the hormone, an ectopic pregnancy (when a pregnancy grows outside of your uterus), or miscarriage.
Whenever there's no gestational sac visible in the uterus, ectopic pregnancy is possible. This happens when the embryo develops somewhere outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes, and .
When a doctor suspects endometrial hyperplasia, they may recommend some additional tests. A transvaginal ultrasound is an imaging tool that shows the inside of the uterus and allows doctors to see if the uterine lining is thicker than it should be. If the uterine lining is too thick, a biopsy of it will be offered to diagnose the condition.
Maria Lozano was already well into menopause when she started experiencing the most common symptom of endometrial cancer (also known as uterine cancer): abnormal vaginal bleeding. “After 10 years of not having my period, suddenly I was bleeding again,” says Maria, who was 59 at the time of her stage III endometrial cancer diagnosis.. “My sister told me I .
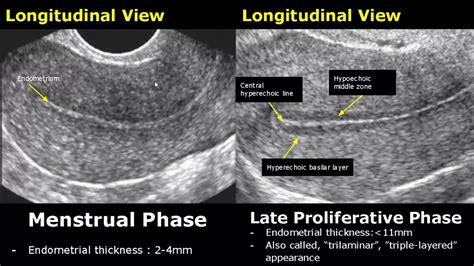
Some of the risk factors for endometrial cancer include the following: Age—Most cases of endometrial cancer are diagnosed after menopause, in your mid-60s.. Levels of hormones—The levels of estrogen and progesterone in your body can affect your risk of endometrial cancer. When estrogen is present without enough progesterone, it can cause the endometrium to .To protect your loved one, please do not visit if you are sick or have a COVID-19 positive test result. Get . (pronounced add-en-o-my-OH-sis) is a gynecologic condition that causes endometrial tissue in the lining of the uterus to grow into the muscular wall of the uterus. . “MRI provides incredibly high-resolution images and shows us the . The uterine lining is called the endometrium. During an imaging test, it’ll show up as a dark line. This is the “endometrial stripe.” Here’s how this tissue can change with age, symptoms . Endometrial thickness is a commonly measured parameter on routine gynecological ultrasound and MRI. The appearance, as well as the thickness of the endometrium, will depend on whether the patient is of reproductive age or postmenopausal and, if of reproductive age, at what point in the menstrual cycle they are examined. . with the .
To perform the test, a health care professional collects a tissue sample from the lining of your uterus, also called the endometrium, and sends the sample to a lab for testing. The test can check for: Endometrial intraepithelial hyperplasia — a precancerous condition in which the uterine lining becomes too thick; Uterine polyps; Uterine cancer
endometrial ultrasound results
With a decidual cast, this thick lining is expelled from your uterus in one large piece of tissue instead of gradually. Its name comes from the scientific name for thickened endometrial tissue, called a decidual lining. The “cast” is because it sheds in almost the same shape (or cast) of your uterine cavity. . Order a pregnancy test. Risks and Complications. While an endometrial biopsy is generally safe, there are some risks and potential complications to be aware of:. Bleeding: Mild spotting or light bleeding is common after the procedure and usually stops within a few days.If you experience heavy or prolonged bleeding, contact your doctor. Infection: Although rare, there’s a small risk of infection.
An endometrial biopsy is a non-surgical procedure that is done to examine and assess the lining of the uterus (endometrium).Your healthcare provider may recommend this test if you have abnormal menstrual or uterine bleeding. They may also recommend it if you have trouble getting pregnant or trouble carrying a pregnancy to term. The main outcome measure was to identify the endometrial thickness and positive pregnancy test which might have ended in miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, preterm, term, or no pregnancy and ongoing viable pregnancy which was confirmed by early USG scan. All data were entered and analyzed through statistical package SPSS version 22. Progesterone is critical in supporting a pregnancy because it thickens your uterine lining. A thick uterine lining helps a fertilized egg grow into an embryo, and then to a fetus. Progesterone levels continue to rise during pregnancy. High progesterone levels prevent your body from ovulating while you’re pregnant.Thick endometrium just means your uterus is rich and ready to nourish an embryo. If they didn't see a sac and you got a positive pregnancy test, then you are probably in the very earliest stages of pregnancy, too early for the other hpt's to pick up! .
One essential cause of concern is the endometrial thickness in pregnancy or the lining of the uterus. Understanding what is normal in terms of endometrial thickness during pregnancy is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how the endometrium changes throughout different stages of pregnancy, what factors can influence its . The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. Its thickness varies with a woman’s age, reproductive stage and specific point of her menstrual cycle. . to prepare the uterus for possible pregnancy. At mid-cycle, the ovary releases an egg during ovulation. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to prepare .Endometrial thickness, pattern, and blood flow, have been used as indicators of endometrial receptivity. While most studies indicate a linear correlation between endometrial thickness and successful implantation, there is disagreement with respect to the ability of endometrial pattern to predict clinical pregnancy. The objective of our study was to examine whether endometrial .
RESULTS: Clinical pregnancy rates are referenced in Table 1. Lining Profile and Clinical Pregnancy Rate Lining Type # of Patients Avg. Age Clinical pregnancy rate (%) A 44 34.1 65.9 B 27 34.3 48.1 C 29 33.7 44.8 Pattern A, endometrial thickness, and E2 were all independently associ-ated with clinical pregnancy (p-values of 0.013, 0.027, and 0. . Endometritis is an inflammation of the uterus lining, also called the endometrium. Learn more about the causes, symptoms, and possible complications here. . Childbirth or pregnancy loss: .Doctors can use it to look at the thickness of the uterine lining or to look at tumors inside the uterus. Ultrasounds also detect ovarian cysts or masses. Endometrial sampling (biopsy): Your doctor performs a pelvic exam and removes a small amount of tissue from the uterine lining, using a small brush or a flexible tube. Cells are scraped from .
Digital Flame Photometer factories
The Luxury Barber Shop. At Miles & Lyle we are bringing back that traditional royal treatment by introducing a full service barbershop in a European flavour. Every detail .
thick endometrial lining positive pregnancy test|endometrial thickness ultrasound